ISO 14126 – Fibre Reinforced Plastic Composite
ISO 14126 specifies two methods for determining compressive properties, in directions parallel to the plane of lamination, of fibre-reinforced plastic composites.
Please Contact With Us For More Information
ISO 14126 – Fibre Reinforced Plastic Composites — Determination of Compressive Properties
in the in-Plane Direction
ISO 14126 specifies two methods for determining compressive properties, in directions parallel to the plane of lamination, of fibre-reinforced plastic composites.
The compressive properties are of interest for specifications and quality-control purposes.
Two loading methods and two types of specimen are described.
They are:
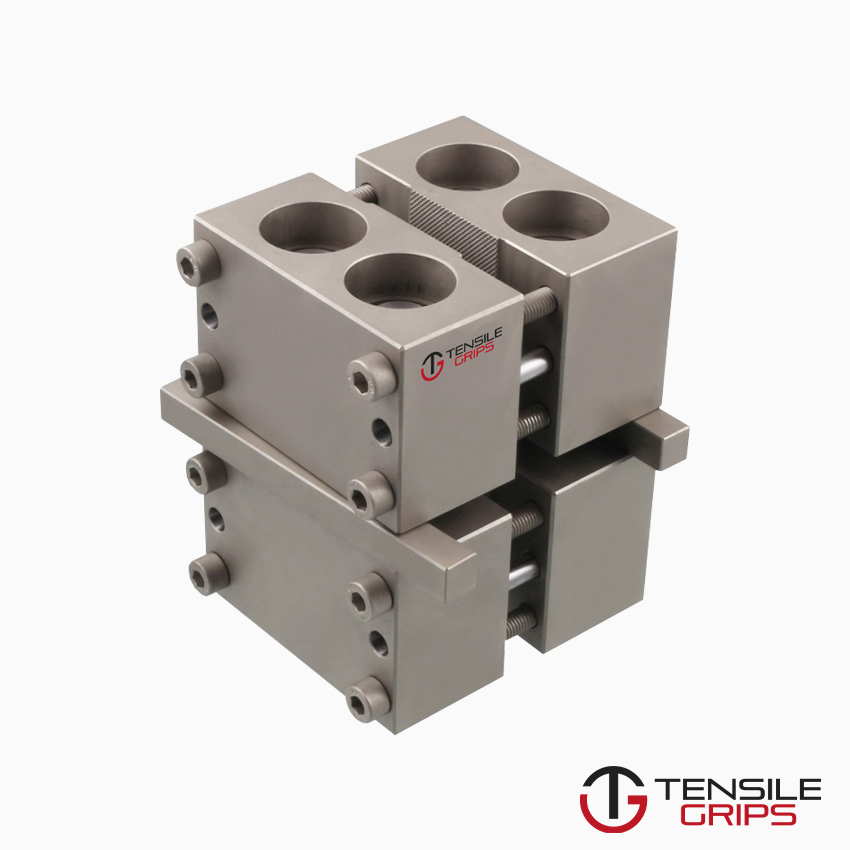
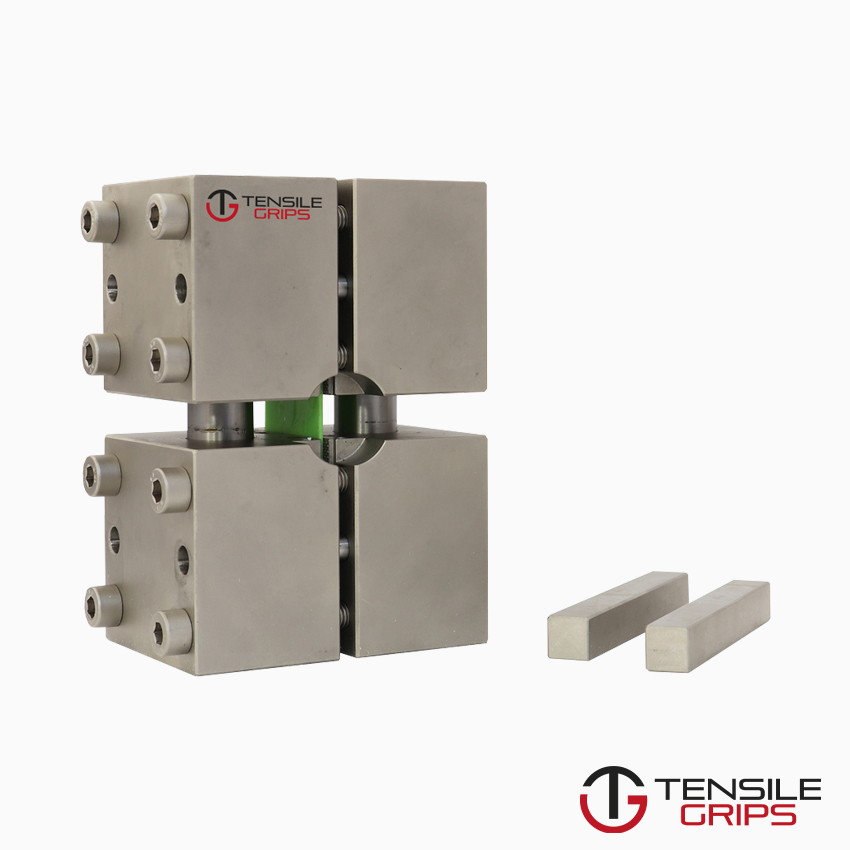
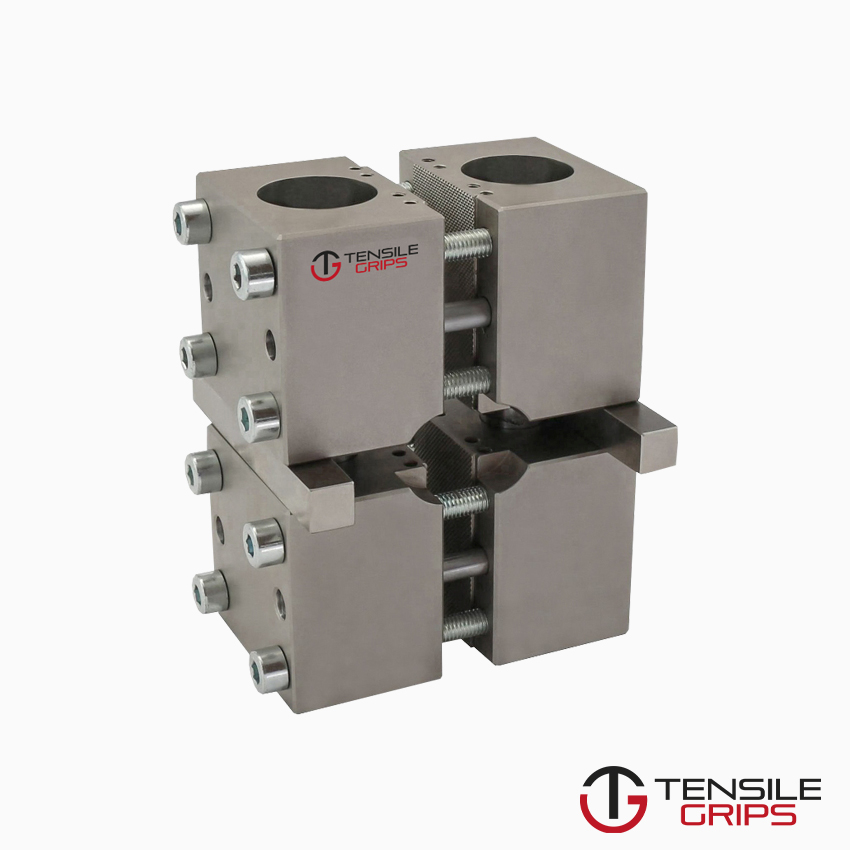
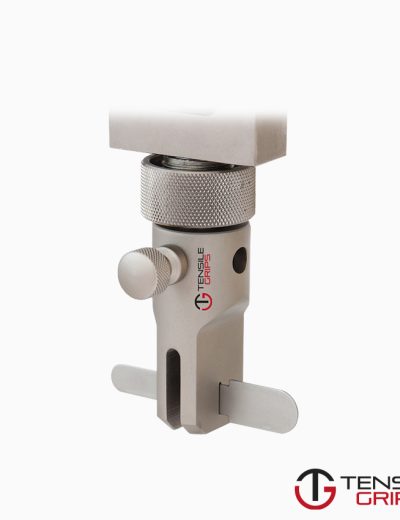
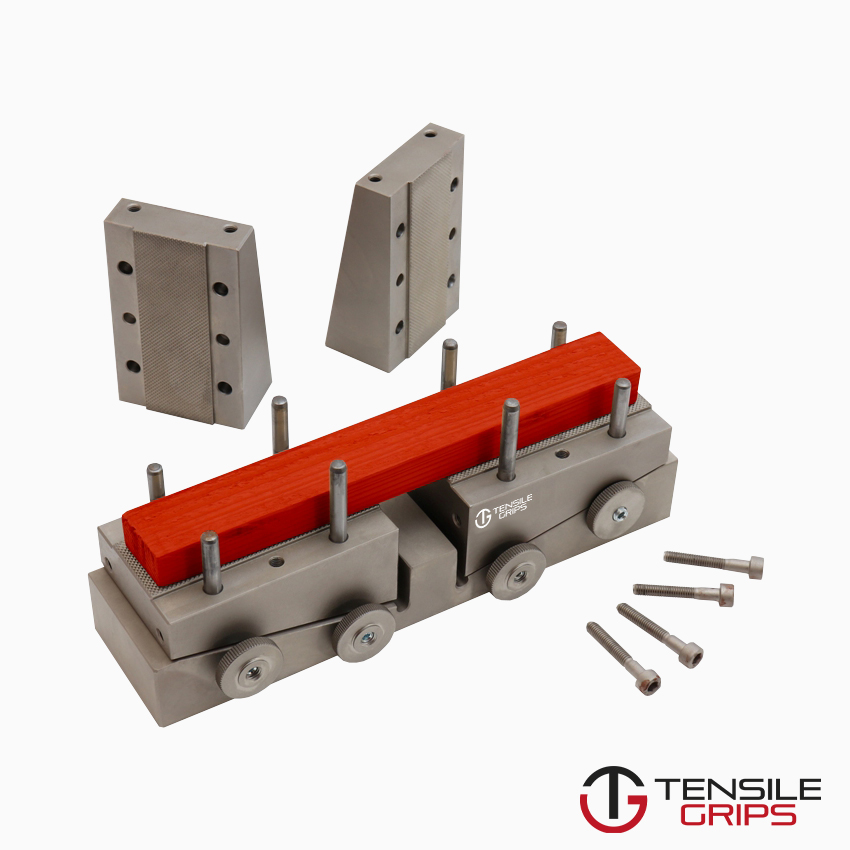
Method 1: provides shear loading of the specimen (gauge length unsupported).
Method 2: provides end loading, or mixed loading, of the specimen (gauge length unsupported).
NOTE : For tabbed specimens end-loaded using method 2, some load is transferred into the specimen gauge length by shear through the tabs.
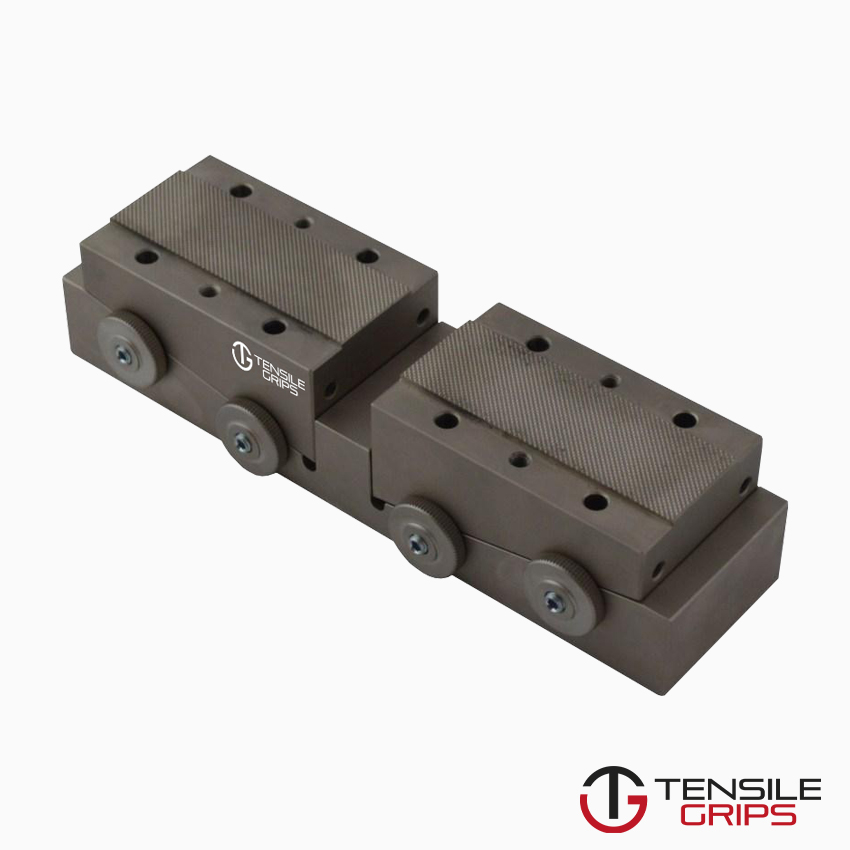
Type A specimen: Rectangular cross-section, fixed thickness, end-tabbed.
Type B specimen: Rectangular cross-section, range of thicknesses, untabbed or end-tabbed (two sizes available).
The type A specimen is the preferred specimen for unidirectionally reinforced materials tested in the fibre direction.
For other materials, the type A or B specimen may be used.
The type B2 specimen is preferred for mat, fabric and other multidirectionally reinforced materials.
The methods are suitable for fibre-reinforced thermoplastic and thermosetting plastic composites.
Unreinforced and particle-filled plastics, as well as those reinforced with short fibres (less than 1 mm in length), are covered by ISO 604
The methods are performed using specimens which may be machined from a test panel made in accordance with ISO 1268 or equivalent methods, or from finished
or semi-finished products.
The methods specify required dimensions for the specimen.
Tests which are carried out on specimens of other dimensions, or on specimens which are prepared under different conditions, may produce results which are not
comparable.
Other factors, such as the speed of testing, the support fixture used and the condition of the specimens, can influence the results.
Consequently, when comparative data are required, these factors must be carefully controlled and recorded.
Fibre-reinforced plastics are usually anisotropic.
It is therefore often useful to cut test specimens in at least the two main directions of anisotropy, or in directions previously specified (for example a lengthwise
direction associated with the production process).
*** Before conducting ISO 14126 , it is important to read the entire specification. Standards can be obtained from appropriate standard authorities.