ASTM D790 Test Fixture
ASTM D790 – This test method is used to determine the flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics, including high modulus composites and electrical insulating
materials
Please Contact With Us For More Information
ASTM D790 – Standard Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics
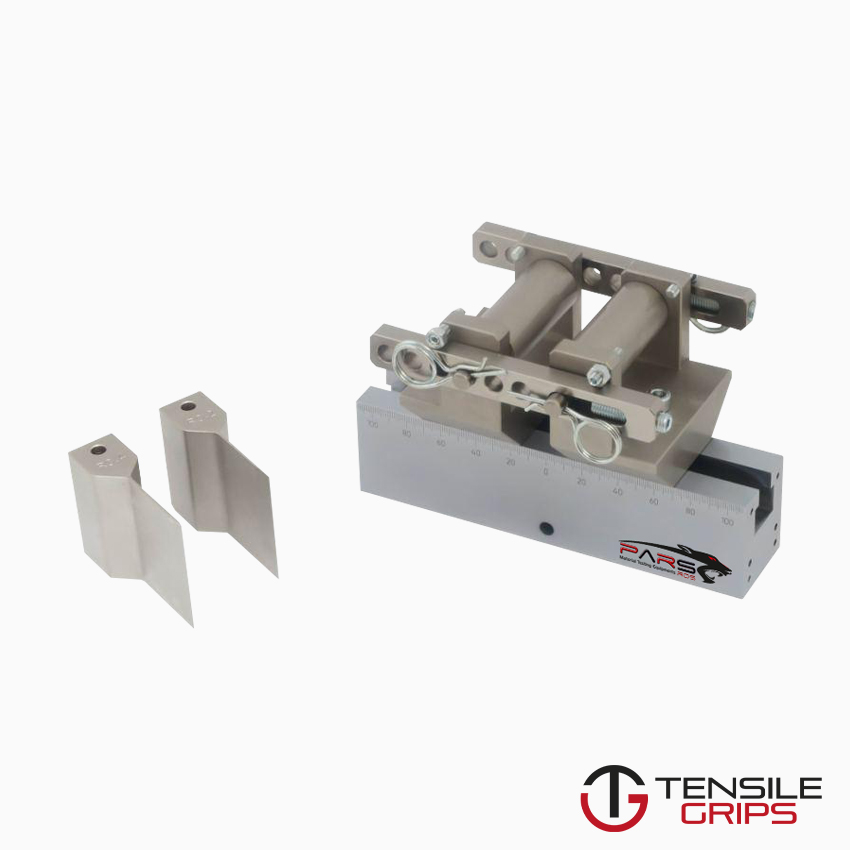
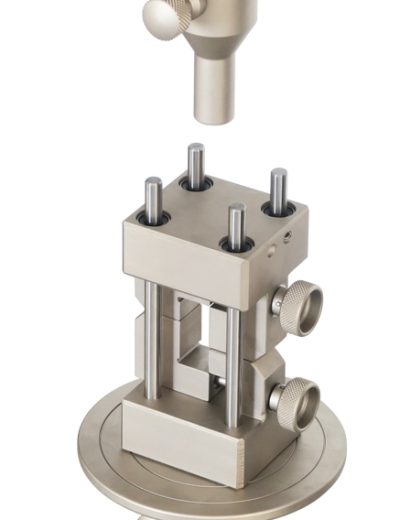
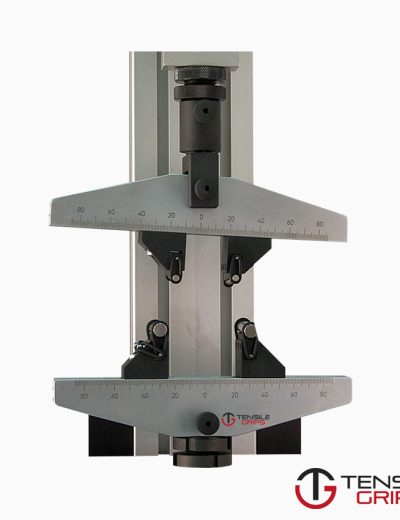
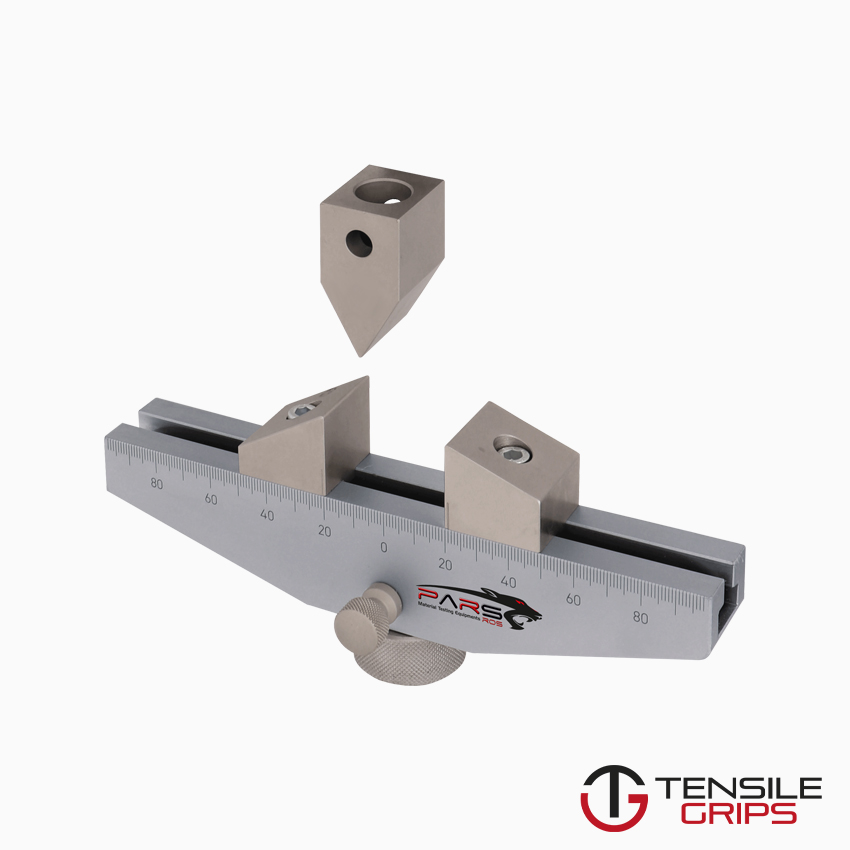
ASTM D790 – Bend Fixture
ASTM D790 – This test method is used to determine the flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics, including high modulus composites and electrical insulating
materials utilizing a three-point loading system to apply a load to a simply supported beam (specimen).
The method is generally applicable to both rigid and semi-rigid materials, but flexural strength cannot be determined for those materials that do not break or yield in
the outer surface of the test specimen within the 5.0 % strain limit.
Test specimens of rectangular cross section are injection molded or, cut from molded or extruded sheets or plates, or cut from molded or extruded shapes.
Specimens must be solid and uniformly rectangular.
The specimen rests on two supports and is loaded by means of a loading nose midway between the supports.
Measure deflection in one of two ways; using crosshead position or a deflectometer
*** Please note that studies have shown that deflection data obtained with a deflectometer will differ from data obtained using crosshead position.
The method of deflection measurement shall be reported.
NOTE 1 : Requirements for quality control in production environments are usually met by measuring deflection using crosshead position.
However, more accurate measurement may be obtained by using an deflection indicator such as a deflectometer.
NOTE 2 : Materials that do not rupture by the maximum strain allowed under this test method may be more suited to a 4-point bend test.
The basic difference between the two test methods is in the location of the maximum bending moment and maximum axial fiber stresses.
The maximum axial fiber stresses occur on a line under the loading nose in 3-point bending and over the area between the loading noses in 4-point bending.
A four-point loading system method can be found in Test Method D6272.
The flexural properties of plastics are measured by most resin suppliers and some of the larger compounders.
The three point bend test is used to determine the flexural strength and modulus of plastic material. The specimen is placed across two bottom support
spans and the third point contacts the sample in the middle from the top.
ASTM D790 – Geometry
There are two types of samples that may be used, either a bar which is longer than it is wide, or a square sheet.
Bars are the most common and tend to be 1/8″ thick.
The distance between the two bottom supports is calculated using a ratio which can be found in the official ASTM specification.
The ratio on length to width can also be found there. The key variable is the cross sectional area of the sample.
ASTM D790 – Solution
The 3 point bend test is rather simple to set up. The plastic sample is placed across the two bottom spans which are adjustable according to the appropriate ratio.
The two bottom span contact points can have rollers in order to better appropriate the normal force, however contact points with a 5mm radius,
ASTM D790 – Analysis
The test is run to 5% strain, of if the sample is brittle, until it breaks. Flexural Strength or Stress is calculated using the method laid out in the ASTM.
The units are represented in MPa (1M newtons per square meter) or in PSI (lbs. per square inch).
Flexural Modulus is a slightly different calculation but just involves dividing the stress delta by the strain delta from the beginning of the test.
Units for flexural modulus are usually much higher and tend to reproted in KSI which is an often confused unit of measurment.
KSI stands for 1,000 lbs. per square inch.