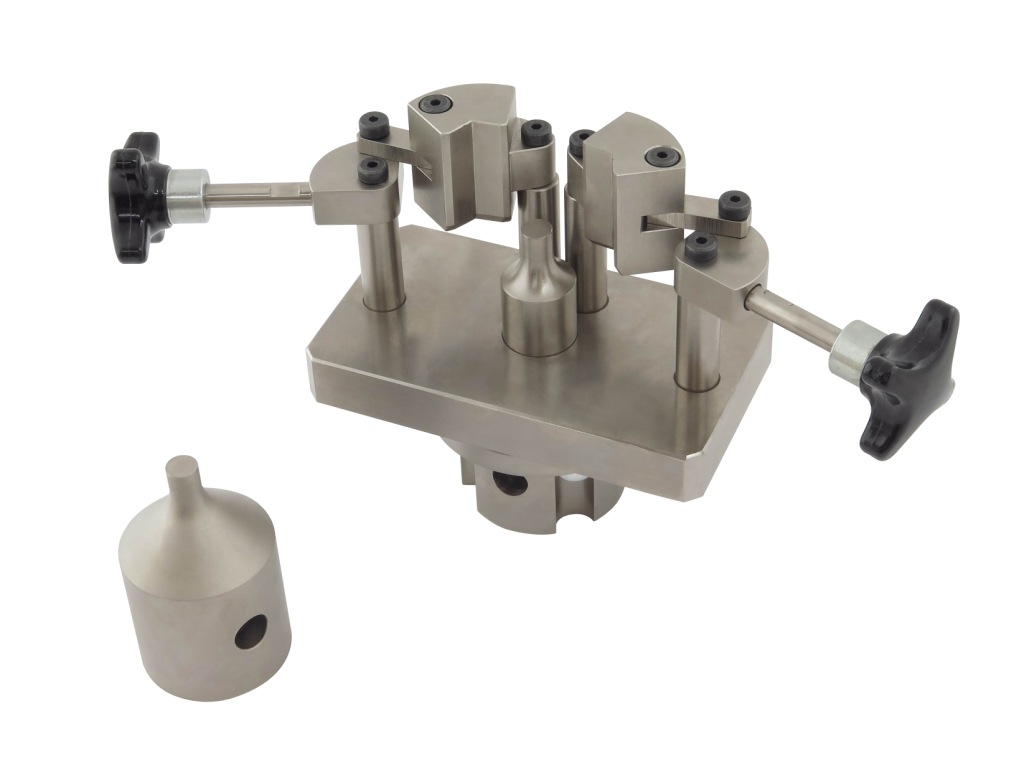
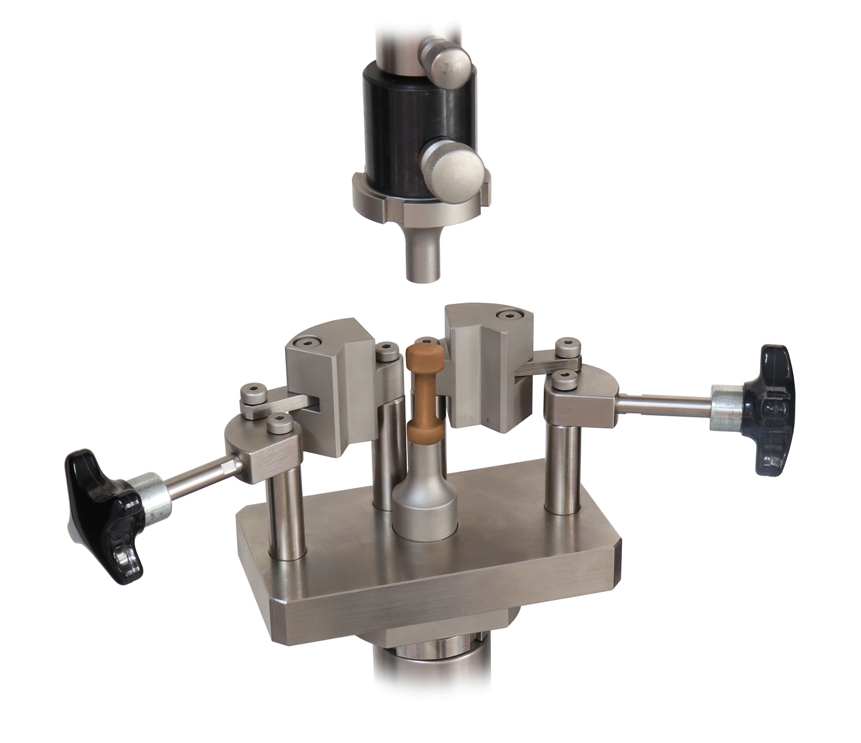
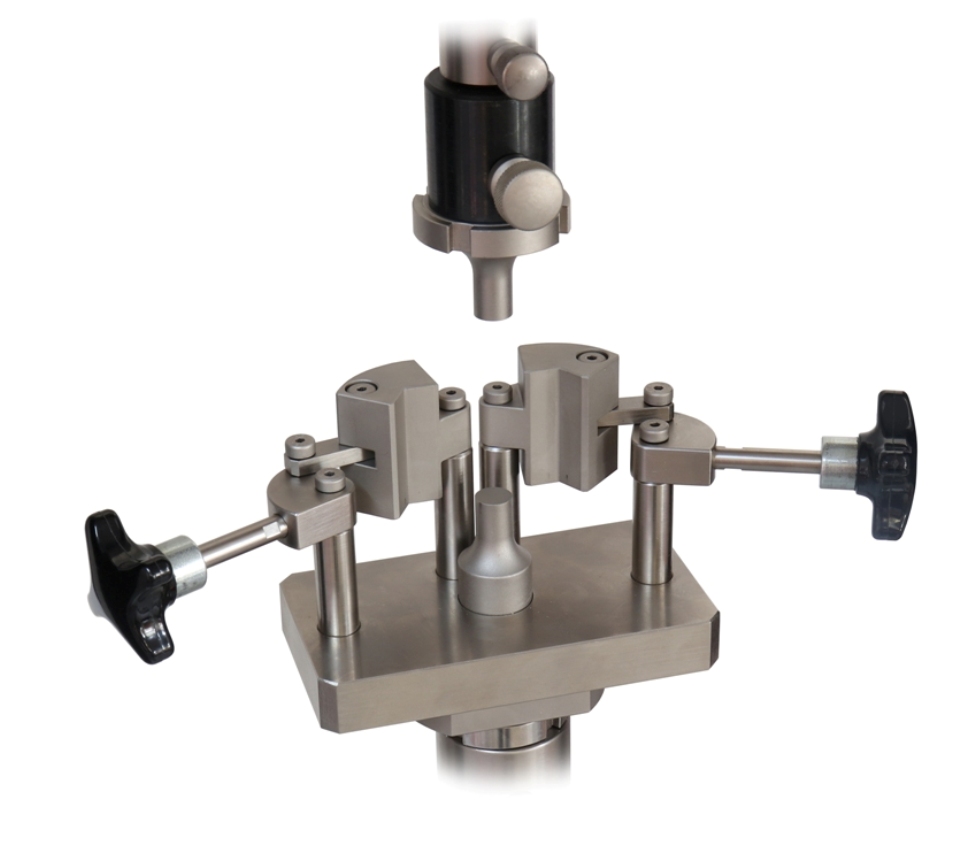
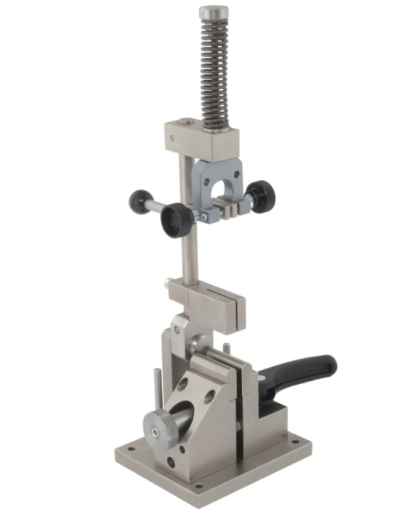
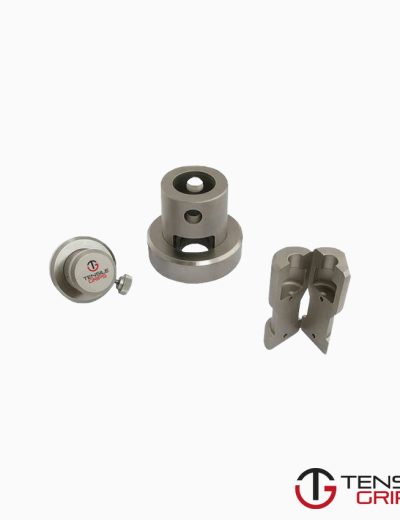
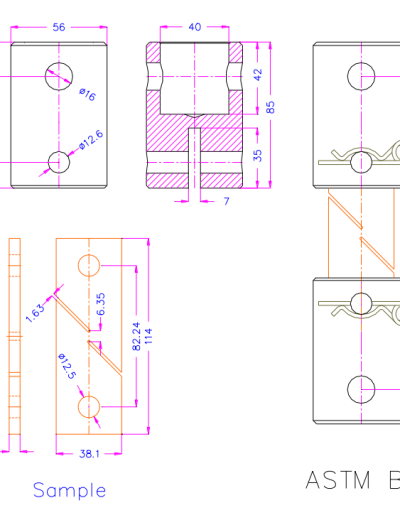
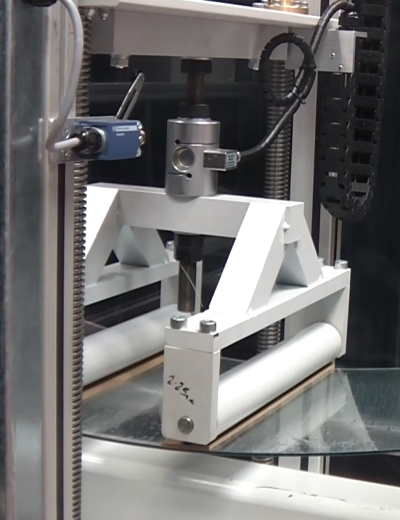
ASTM C1424 Test Fixture
ASTM C1424 covers the determination of compressive strength including stress-strain behavior, under monotonic uniaxial loading of advanced ceramics
at ambient temperature.
Please Contact With Us For More Information
ASTM C1424 Standard Test Method for Monotonic Compressive Strength of Advanced Ceramics at Ambient Temperature
ASTM C1424 covers the determination of compressive strength including stress-strain behavior, under monotonic uniaxial loading of advanced ceramics
at ambient temperature.
This test method is restricted to specific test specimen geometries.
In addition, test specimen fabrication methods, testing modes (load or displacement), testing rates (load rate, stress rate, displacement rate, or strain rate),
allowable bending, and data collection and reporting procedures are addressed.
Compressive strength as used in this test method refers to the compressive strength obtained under monotonic uniaxial loading.
Monotonic loading refers to a test conducted at a constant rate in a continuous fashion, with no reversals from test initiation to final fracture
ASTM C1424 / Apparatus
Testing Machines
Machines used for compression testing shall conform to the requirements.
The forces used in determining compressive strength shall be accurate within 61 % at any force within the selected force range of the testing machine .
Check that the expected breaking force for the desired test specimen geometry and test material is within the capacity of the test machine and force transducer.
Advanced ceramic compression test specimens require much greater forces to fracture than those usually encountered in tension or flexure test specimens of
the same material.
ASTM C1424 / Loading Fixtures
Compression loading fixtures are generally composed of two parts:
(1) Basic steel compression fixtures (for example, platens) attached to the test machine and
(2) Loading blocks which are non-fixed and act as the interface between the compression platens and the test specimen.
The brittle nature of advanced ceramics requires a uniform interface between the loading fixtures and the test specimen.
Line or point contact stresses lead to crack initiation and fracture of the test specimen at stresses less than the actual compressive strength (that is, where actual
strength is theintrinsic strength of the material not influenced by the test or test conditions). In addition, large mismatches of Poisson’s ratios or elastic moduli
between the loading fixture and testspecimen, or both, can introduce lateral tensile forces leading to splitting of the compression test specimen. Similarly, plastic
deformation of the load fixture can induce lateral tensile forces with the same effect.
*** Before conducting ASTM C1424 , it is important to read the entire specification. Standards can be obtained from appropriate standard authorities.